neo_goal_sequence_driver¶
Summary¶
The neo_goal_sequence_driver package is a exclusively ROS-1 only package, that provides a means to command a user defined sequence of goals, optionally in a looped mode too.
Tip
Prerequisite knowledge: Installation and Navigation with Move Base for neo_simulation package
Location: https://github.com/neobotix/neo_goal_sequence_driver
Attention
Currently neo_goal_sequence_driver only supports ROS-1
Nodes¶
- Services:
- /goal_sequence_driver/run
- /goal_sequence_driver/stop
- Parameters:
- The following parameters could be found in driver_config.yaml and can be modified:
| Parameter | Default | Description | Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| infi_param | false | Robot will (or not) continuously repeat the sequence until it’s shutdown by calling service. | true, false |
| manual_stepping | false | if to require calling /next for each goal | bool |
| patience | 5 | User can define the time length spent on one single goal (in seconds). | integer |
| print_option | all | User can define which information is to be printed in terminal. | local, total, all |
Usage¶
Initial Startup¶
Start the robot (or simulator) and launch navigation stack first, e.g. using simulator:
roslaunch neo_simulation simulation.launch
Goal Configuration¶
Goals to the driver can be given in two ways:
Manual¶
Manual methodology will allow the users to set the co-ordinates of the goals by directly editing the YAML file
roslaunch neo_goal_sequence_driver neo_goal_sequence_driver.launch
Note
You should have the basic navigation bringup already running.
Automated¶
Automated methodology will allow the users to set the goals on the fly in RViz.
Note
In order to use the functionality in simulation, set the “move_base” argument to “false” in the ($Desire_robot)_autonomous_navigation.launch file.
For the real robot, just start the neo_localization node : (if you have mp_500, use the below command! Else, change it based on your robot type)
roslaunch neo_mp_500 neo_localization.launch
Now run:
roslaunch neo_goal_sequence_driver neo_goal_sequence_driver_autoamated.launch
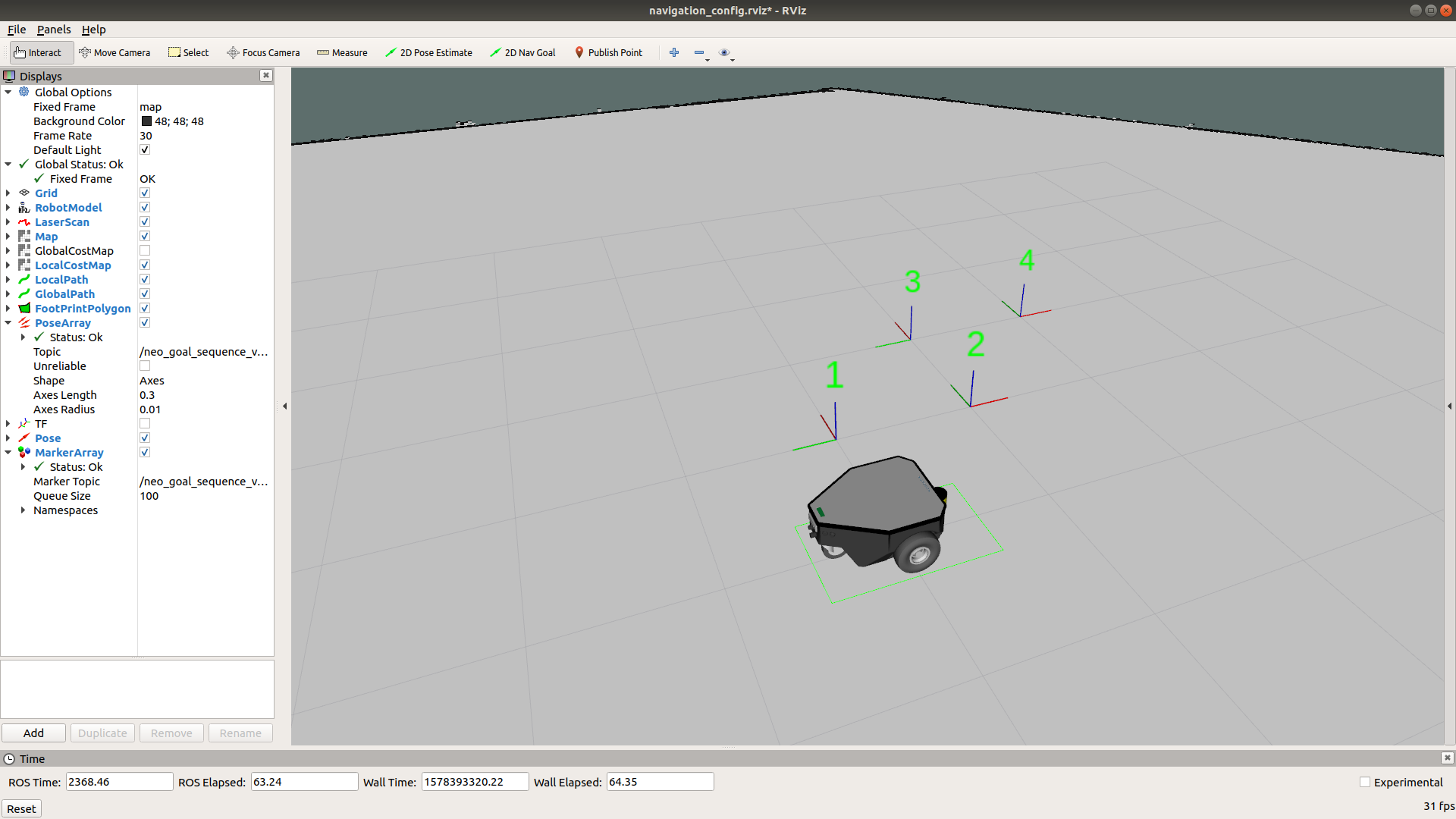
automated_sequence node enables to use the “2D Nav goal” option to continuously set any number of goals in sequence which are then visualized using the pose arrays.
Node updates the selected goal sequence in the YAML file.
In simulation run:
roslaunch neo_simulation ($Desire_robot)_move_base.launch
In real-robot now run: (if you have mp_500, use the below command! Else, change it based on your robot type)
roslaunch neo_mp_500 move_base.launch
Setup server¶
Run goal_sequence_driver_server and goal_sequence_visualizer with launch file:
roslaunch neo_goal_sequence_driver neo_goal_sequence_driver_visualized.launch
if the visualization of goal list is not necessary, just launch the server by:
roslaunch neo_goal_sequence_driver neo_goal_sequence_driver.launch
Warning
Make sure the system time on the platform is the same as on the machine which is running neo_goal_sequence_driver, otherwise it may not work.
If every thing is now set up, it looks like the picture below, you can move on to next step and demand the robot to first goal!
Change configurations:
- shutdown the server node
- modify yaml files
- run server node again
Start driver¶
Start the driver by calling:
rosservice call /goal_sequence_driver/run
Now the robot should be moving toward it’s goals until it reaches the final one(if the default configurations are applied).
Stop by calling:
rosservice call /goal_sequence_driver/stop
And if the former service is called again, it restarts the drive from 1st goal.